The Dictatorship
Zelenskyy to meet with Trump as efforts to end Russia-Ukraine war remain elusive

PALM BEACH, Fla. (AP) — President Donald Trump on Sunday insisted Ukraine and Russia are “closer than ever before” to a peace deal as he hosted Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy at his Florida resort, but he acknowledged the negotiations are complex and could still break down, leaving the war dragging on for years.
The president’s statements came after the leaders met for talks following what Trump said was an “excellent,” two-and-a-half-hour phone conversation with Russian President Vladimir Putin, whose invasion of Ukraine launched the war nearly four years ago. Trump insisted he believed Putin still wants peace, even as Russia launched another round of attacks on Ukraine while Zelenskyy flew to the United States for the latest round of negotiations.
“Russia wants to see Ukraine succeed,” Trump said during a late afternoon news conference as he stood with Zelenskyy after their meeting. He repeatedly praised his counterpart as “brave.”
Trump and Zelenskyy both acknowledged thorny issues remain, including whether Russia can keep Ukrainian territory it controls, as well as security guarantees for Ukraine to ensure it’s not invaded again in the future. After their discussion, they called a wide group of European leaders, including Ursula von der Leyen, president of the European Commission, and the leaders of Finland, France, Germany, the United Kingdom and Poland.
Zelenskyy said Trump had agreed to host European leaders again, possibly at the White House, sometime in January. Trump said the meeting could be in Washington or “someplace.”
Zelenskyy thanked Trump for his work. “Ukraine is ready for peace,” he said.
Trump and Putin will speak again
Trump said he’d follow the meeting with another call to Putin. Earlier Sunday, Putin’s foreign affairs adviser Yuri Ushakov said the Trump-Putin call was initiated by the U.S. side and was “friendly, benevolent and businesslike.” Ushakov said Trump and Putin agreed to speak again “promptly” after Trump’s meeting with Zelenskyy.
But Ushakov added that a “bold, responsible, political decision is needed from Kyiv” on the fiercely contested Donbas region in eastern Ukraine and other matters in dispute for there to be a “complete cessation” of hostilities.
Both leaders identified deciding the future of the Donbas region as a major sticking point.
Trump said the parties were inching closer to agreement. “That’s a very tough issue but one that I think will get resolved,” he said.
Zelenskyy said: “Our attitude is very clear. That’s why President Trump said this is a very tough question and, of course, we have with Russia different positions on it.”
Trump said, however, that he still believes Putin is “very serious” about ending the war, even as Russia continued striking targets in Ukraine as Zelenskyy traveled to the U.S. Trump said, “I believe Ukraine has made some very strong attacks also.”
He held out the possibility that negotiations could still fall apart.
“In a few weeks, we will know one way or the other, I think,” Trump said. “We could have something where one item that you’re not thinking about is a big item, breaks it up. Look, it’s been a very difficult negotiation. Very detailed.”
Trump and Zelenskyy’s sit-down underscored the apparent progress made by Trump’s top negotiators in recent weeks as the sides traded draft peace plans to end the fighting. Zelenskyy told reporters Friday that the 20-point draft proposal negotiators have discussed is “about 90% ready” — echoing a figure, and the optimism, that U.S. officials conveyed when Trump’s chief negotiators met with Zelenskyy in Berlin this month.
During the recent talks, the U.S. agreed to offer certain security guarantees to Ukraine similar to those offered to other members of NATO. The proposal came as Zelenskyy said he was prepared to drop his country’s bid to join the security alliance if Ukraine received NATO-like protection that would be designed to safeguard it against future Russian attacks.
‘Intensive’ weeks ahead
Zelenskyy also spoke on Christmas Day with U.S. special envoy Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner, Trump’s son-in-law. The Ukrainian leader said they discussed “certain substantive details” and cautioned “there is still work to be done on sensitive issues” and “the weeks ahead may also be intensive.”
The U.S. president has been working to end the war in Ukraine for much of his first year back in office, showing irritation with both Zelenskyy and Putin while publicly acknowledging the difficulty of ending the conflict. Gone are the days when, as a candidate in 2024, he boasted that he could resolve the fighting in a day. Indeed, on Sunday, Trump referred multiple times to the complexity of the negotiations.
After hosting Zelenskyy at the White House in OctoberTrump demanded that both Russia and Ukraine halt fighting and “stop at the battle line,” implying that Moscow should be able to keep the territory it has seized from Ukraine.
Zelenskyy said last week that he would be willing to withdraw troops from Ukraine’s eastern industrial heartland as part of a plan to end the war, if Russia also pulls back and the area becomes a demilitarized zone monitored by international forces.
Putin wants Russian gains kept, and more
Putin has publicly said he wants all the areas in four key regions that have been captured by his forces, as well as the Crimean Peninsula, illegally annexed in 2014, to be recognized as Russian territory. He also has insisted that Ukraine withdraw from some areas in eastern Ukraine that Moscow’s forces haven’t captured. Kyiv has publicly rejected all those demands.
The Kremlin also wants Ukraine to abandon its bid to join NATO. It warned that it wouldn’t accept the deployment of any troops from members of the military alliance and would view them as a “legitimate target.”
Putin also has said Ukraine must limit the size of its army and give official status to the Russian language, demands he has made from the outset of the conflict.
Ushakov told the business daily Kommersant this month that Russian police and national guard would stay in parts of Donetsk -– one of the two major areas, along with Luhansk, that make up the Donbas region — even if they become a demilitarized zone under a prospective peace plan.
Ushakov cautioned that trying to reach a compromise could take a long time. He said U.S. proposals that took into account Russian demands had been “worsened” by alterations proposed by Ukraine and its European allies.
Trump has been somewhat receptive to Putin’s demands, arguing that the Russian president can be persuaded to end the war if Kyiv agrees to cede Ukrainian land in the Donbas region and if Western powers offer economic incentives to bring Russia back into the global economy.
___
Kim reported from Washington and Morton from London. Associated Press writers Illia Novikov in Kyiv, Nicholas Riccardi in Denver and Darlene Superville in Washington contributed to this report.
The Dictatorship
Congress taking first votes on Iran war as debate rages about US goals

WASHINGTON (AP) — Senate Republicans voted down an effort Wednesday to halt President Donald Trump’s war against Irandemonstrating early support for a conflict that has rapidly spread across the Middle East with no clear U.S. exit strategy.
The legislation, known as a war powers resolutionfailed on a 47-53 vote tally. The vote fell mostly along party lines, though Republican Sen. Rand Paul of Kentucky voted in favor and Democratic Sen. John Fetterman of Pennsylvania voted against.
The war powers resolution gave lawmakers an opportunity to demand congressional approval before any further attacks are carried out. The vote forced them to take a stand on a war shaping the fate of U.S. military members, countless other lives and the future of the region.
Underscoring the gravity of the moment, Democratic senators filled the Senate chamber and sat at their desks as the voting got underway. Typically, senators step into the chamber to cast their vote, then leave.
House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries, D-N.Y., speaks to reporters during a news conference on Capitol Hill in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/Manuel Balce Ceneta)
House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries, D-N.Y., speaks to reporters during a news conference on Capitol Hill in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/Manuel Balce Ceneta)
“Today every senator — every single one — will pick a side,” Senate Democratic Leader Chuck Schumer said before the vote. “Do you stand with the American people who are exhausted with forever wars in the Middle East or stand with Donald Trump and Pete Hegseth as they bumble us headfirst into another war?”
Sen. John Barrasso, second in Senate Republican leadership, said during the debate that GOP senators were sending a message that Democrats are wrong for forcing a vote on the war powers resolution.
“Democrats would rather obstruct Donald Trump than obliterate Iran’s national nuclear program,” he added.
Trump administration scrambles for congressional support
AP AUDIO: Congress is taking its first votes on the Iran war as debate rages about US goals
AP Washington correspondent Sagar Meghani reports on Congress weighing in amid the war against Iran.
After launching a surprise attack against Iran on Saturday, Trump has scrambled to win support for a conflict that Americans of all political persuasions were already wary of entering. Trump administration officials have been a frequent presence on Capitol Hill this week as they try to reassure lawmakers that they have the situation under control.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said Wednesday that the war could extend eight weeks, a longer time frame than has previously been floated by the Trump administration. He also acknowledged that Iran is still able to carry out missile attacks even as the U.S. tries to control the country’s airspace.
U.S. service members “remain in harm’s way, and we must be clear-eyed that the risk is still high,” Gen. Dan Caine, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, said at the same press conference.
Six U.S. military members were killed over the weekend in a drone strike in Kuwait.
Republican Sen. Joni Ernst of Iowa acknowledged the human costs of the war in her floor speech. Two of the soldiers killed Sunday were from Iowa and a National Guard unit from her state was also attacked in Syria in December, resulting in the deaths of two other soldiers.
“But now is our opportunity to bring an end to the decades of chaos,” said Ernst, who herself served as an officer in the Iowa National Guard for two decades.
“The sooner the better,” she added.
Trump has also not ruled out deploying U.S. ground troops. He has said he is hoping to end the bombing campaign within a few weeks, but his goals for the war have shifted from regime change to stopping Iran from developing nuclear capabilities to crippling its navy and missile programs.
Senate Majority Leader John Thune, R-S.D., center, joined at left by Sen. John Barrasso, R-Wyo., the GOP whip, speaks to reporters at the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Senate Majority Leader John Thune, R-S.D., center, joined at left by Sen. John Barrasso, R-Wyo., the GOP whip, speaks to reporters at the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
“We should be careful about opening a door into chaos in the Middle East when we cannot see the other side of it,” Democratic Sen. Chris Coons of Delaware said in a solemn floor speech after the vote concluded.
He said he was praying for “grace to find a path forward together where more do not needlessly join those who have already fallen in this new war in the Middle East.”
Lawmakers go on record
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth arrives for a briefing for lawmakers on Iran at a secure room in the basement of the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth arrives for a briefing for lawmakers on Iran at a secure room in the basement of the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
The votes in Congress this week represented potentially consequential markers of just where lawmakers stand on the war as they look ahead to midterm elections and the consequences of the conflict.
“Nobody gets to hide and give the president an easy pass or an end-run around the Constitution,” said Sen. Tim Kaine, the Virginia Democrat leading the war powers resolution.
Republican leaders have successfully, though narrowly, defeated a series of war powers resolutions pertaining to several other conflicts that Trump has entered or threatened to enter. This one, however, was different.
Unlike Trump’s military campaigns against alleged drug boats or even Venezuelan leader Nicolás Maduro, the attack on Iran represents an open-ended conflict that is already ricocheting across the region. Several senators who have voted for previous war powers resolutions noted that they opposed this one because it applied to a conflict that is already raging.
“Passing this resolution now would send the wrong message to Iran and to our troops,” said GOP Sen. Susan Collins of Maine. “At this juncture, providing unequivocal support to our service members is critically important, as is ongoing consultation by the administration with Congress.”
House vote looms
On the other side of the Capitol, an intense debate over the war unfolded before a vote Thursday. The House first debated a resolution presented by GOP leadership affirming that Iran is the world’s largest state sponsor of terrorism.
Rep. Brian Mast, the GOP chairman of the House Foreign Affairs Committee, publicly thanked Trump for taking action against Iran, saying the president is using his own constitutional authority to defend the U.S. against the “imminent threat” of Iran.
Mast, an Army veteran who worked as a bomb disposal expert in Afghanistan, said the Democratic resolution was effectively asking “that the president do nothing.”
Rep. Gregory Meeks, the top Democrat on the Foreign Affairs panel, said before the debate that the hardest votes he has taken in Congress have been to decide whether to send U.S. troops to war. “Our young men and women’s lives are on the line,” he said, his voice showing emotion as he emerged from a closed-door bri efing late Tuesday with Trump officials.
At a news conference Wednesday, several Democratic members who are also veterans of the Iraq and Afghanistan wars spoke about the heavy costs of those conflicts.
One of them was Rep. Jason Crow, D-Colo. “I learned when I was fighting in Iraq and Afghanistan, that when elites in Washington bang the war drums, pound their chest, talk about the costs of war and act tough, they’re not talking about them doing it, they’re not talking about their kids,” Crow said. “They’re talking about working class kids like us.”
The Dictatorship
TENSIONS FLARE ON HILL
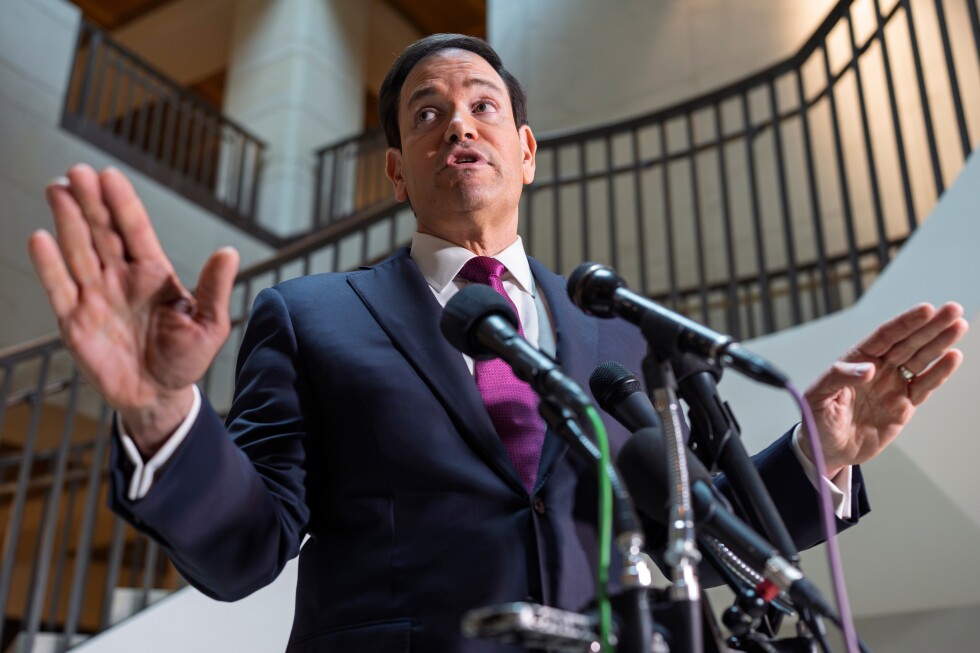
WASHINGTON (AP) — Tensions flared as questions mounted at the U.S. Capitol on Tuesday over the Trump administration’s shifting rationale for war with Iran as lawmakers demand answers over the strategy, exit plan and costs to Americans in lives and dollars for what is quickly becoming a widening Middle East conflict.
Trump officials made their case at the Capitol during a second day of closed-door briefings, this time with all members of the House and Senate ahead of a looming war powers resolution vote intended to restrict Trump’s ability to continue the joint U.S.-Israel campaign against Iran.
“The president determined we were not going to get hit first. It’s that simple,” Secretary of State Marco Rubio said in a testy exchange with reporters at the Capitol.
Rubio pushed back on his own suggestion a day earlier that Trump decided to strike Iran because Israel was ready to act first. Instead, he said Trump made the decision to attack this past weekend because it presented a unique opportunity with maximum chance for success.
“There is no way in the world that this terroristic regime was going to get nuclear weapons, not under Donald Trump’s watch,” he said.
The sudden pivot to a U.S. wartime footing has disrupted the political and policy agenda on Capitol Hill and raised uneasy questions about the risks ahead for a prolonged conflict and regime change after the killing of Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. At least six U.S. military service personnel have died so far.
The situation has intensified the push in Congress for the war powers resolution — among the most consequential votes a lawmaker can take, with the war well underway — as administration officials are telling lawmakers they will likely need supplemental funds to pay for the conflict. It comes at the start of a highly competitive midterm election season that will test Trump’s slim GOP control of Congress.
Senate Democratic Leader Chuck Schumer left the closed hearing, saying he was concerned about “mission creep” in a long war.
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth arrives for a briefing for lawmakers on Iran at a secure room in the basement of the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth arrives for a briefing for lawmakers on Iran at a secure room in the basement of the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Senators demand answers, and some cheer Trump on
Senators spent the morning grilling Trump officials during an Armed Services Committee hearing over Rubio’s claim Monday that the president, believing that Israel was ready to act, decided it was better for the U.S. to launch a preemptive strike to prevent Iran’s potential retaliation on American military bases and interests abroad.
Sen. Angus King, the independent from Maine, said it’s “very disturbing” that Trump took the U.S. to war because Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu wanted to bomb Iran. Past U.S. presidents, he said, “have consistently said, ‘No.’”
Defense official Elbridge Colby told senators the president directed the military campaign to destroy Iranian missiles and deny the country nuclear weapons.
Trump himself disputed the idea that Israel had forced his hand. In his own Oval Office remarks, he said, “I might might have forced their hand.”
Sen. Markwayne Mullin, a Trump ally from Oklahoma, said the president “did the world a favor.”
“How about we say, ‘Thank you, Mr. President, for finally getting rid of this nuisance,’” he said.
But Sen. Elizabeth Warren, D-Mass., demanded to know how this fits into Trump’s “America First” campaign promise not to commit U.S. troops to protracted military campaigns abroad.
Trump has suggested the war could drag on, and has not ruled out sending American troops into Iran.
“’America First’ and ‘peace through strength’ are served by rolling back — as the military campaign is designed to do — the threats posed,” Colby responded. “This is certainly not nation-building. This is not going to be endless.”
Senate Majority Leader John Thune, R-S.D., arrives for a briefing for Senators on Iran at a secure room in the basement of the Capitol in Washington, Tuesday, March 3, 2026. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
Senate Intelligence Committee Sen. Mark Warner, D-Va., speaks to reporters following a House and Senate Intelligence Committees briefing about the war in Iran at the Capitol in Washington, Monday, March 2, 2026. (AP Photo/Manuel Balce Ceneta)
What’s next for the Iranian regime and its people
Questions are growing over who will lead Iran after the death of Khamenei, who has ruled the country for decades, and worries of a leadership vacuum that creates unrest.
Democrats warned against sending U.S. military troops into Iran after more than two decades of war in Iraq and Afghanistan in the aftermath of the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks.
“I am more fearful than ever we may be putting boots on the ground,” said Sen. Richard Blumenthal, D-Conn., after the closed briefing.
And while House Republicans applauded in support of the Trump administration’s operations, warning signs flared.
Rep. Chip Roy, R-Texas, said he supports the operation, for now. “My flag starts going up, the longer this goes, my flag starts going up, the more there’s boots on the ground,” he said.
Many lawmakers expressed concern over the number of Americans calling their offices seeking help evacuating from the region as the war spreads. “It’s getting worse, not better,” said Rep. Jason Crow, D-Colo., a former Army Ranger.
Trump, in calling for Iranians to seize this opportunity to take back their country, has acknowledged the uncertainty.
“Most of the people we had in mind are dead,” Trump said Tuesday. He also panned the idea of elevating Reza Pahlavi, the exiled crown prince of Iran’s last shah, to take over in Iran.
Republicans insist it’s not for the Americans to decide the future of Iran.
“That’s going to be largely up to the Iranian people,” said Senate Majority Leader John Thune, a Republican.
House Speaker Mike Johnson said flatly, “We have no ability to get into the nation-building business.”
President Donald Trump departs after a Medal of Honor ceremony in the East Room of the White House, Monday, March 2, 2026, in Washington. (AP Photo/Alex Brandon)
President Donald Trump departs after a Medal of Honor ceremony in the East Room of the White House, Monday, March 2, 2026, in Washington. (AP Photo/Alex Brandon)
War powers resolutions become a consequential vote
Both the House and Senate are preparing to vote on war powers resolutions that would restrain Trump’s ability to continue waging war on Iran without approval from Congress.
Under the U.S. Constitution, it’s up to Congress, not the president, to decide when the country goes to war. But lawmakers often shirk that duty, enabling the executive branch to amass more power to send the military into combat without congressional approval.
“Why are we spending billions of dollars to bomb Iran?” said House Democratic Leader Hakeem Jeffries, who said there would be strong support from Democrats for the resolution.
But Johnson has said it would be “frightening” and “dangerous” to tie the president’s hands at this time, when the U.S. is already engaged in combat.
Other lawmakers have suggested that if Congress does not vote to restrain Trump, it should next consider an Authorization of the Use of Military Force, which would require lawmakers to go on record with affirmative support for the Iran operation.
“The reason why there’s so much consternation on our side is because President Trump has not given us a clear reason why he is in Iran,” said Sen. Kirsten Gillibrand, D-N.Y. “If he wants to declare war on Iran, that is the job and responsibility of Congress under the Constitution.”
Former President George W. Bush sought, and received, authorization from Congress to launch the post-9/11 wars.
___
Associated Press writers Stephen Groves and Mary Clare Jalonick contributed to this report.
The Dictatorship
Trump threatens to cut off trade with Spain

WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump on Tuesday threatened to end trade with Spainciting a lack of support over the U.S. and Israeli attacks on Iran and the European nation’s resistance to increasing its NATO spending.
“We’re going to cut off all trade with Spain,” Trump told reporters during an Oval Office meeting with German Chancellor Friedrich Merz. “We don’t want anything to do with Spain.”
The U.S. president’s comments came a day after Spanish Foreign Minister José Manuel Albares said his country would not allow the U.S. to use jointly operated bases in southern Spain in any strikes not covered by the United Nations’ charter. Albares noted that the military bases in Spain were not used in the weekend attack on Iran.
Trump said despite Spain’s refusal “we could use their base if we want. We could just fly in and use it. Nobody’s going to tell us not to use it, but we don’t have to.”
It is unclear how Trump would cut off trade with Spain, given that Spain is under the umbrella of the European Union. The EU negotiates trade deals on behalf of all 27 member countries.
“If the U.S. administration wishes to review the trade agreement, it must do so respecting the autonomy of private companies, international law, and bilateral agreements between the European Union and the United States,” a spokesperson from Spanish Prime Minister Pedro Sánchez’s office said Tuesday.
The EU said it expects the Trump administration to honor a trade deal struck with the 27-nation bloc in Scotland last year after months of economic uncertainty over Trump’s tariff blitzkrieg.
“The Commission will always ensure that the interests of the European Union are fully protected,” said European Commission spokesperson Olof Gill.
It was just the latest instance of the president wielding the threat of tariffs or trade embargoes as a punishment and came on the heels of a Supreme Court decision that struck down Trump’s far-reaching global tariffs. While the court said that the International Emergency Economic Powers Act does not authorize the president to unilaterally impose sweeping tariffs, Trump now maintains that the court allows him to instead impose full-scale embargoes on other nations of his choosing.
Trump also complained anew Tuesday about Spain’s decision last year to back out of NATO’s 5% defense spending target. At the time, Spain said it could reach its military capabilities by spending 2.1% of its GDP, a move that Trump roundly criticized and responded to with tariff threats as well.
Spain, Trump said, is “the only country that in NATO would not agree to go up to 5%” in NATO spending. “I don’t think they agreed to go up to anything. They wanted to keep it at 2% and they don’t pay the 2%.”
Merz noted that Trump was correct and said, “We are trying to convince them that this is a part of our common security, that we all have to comply with this.”
Spain defended its position Tuesday, saying it is “a key member of NATO, fulfilling its commitments and making a significant contribution to the defense of European territory,” the spokesperson in Sánchez’s office said.
During the Oval Office meeting, Trump turned to U.S. Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent for his opinion on the president’s embargo authority.
Bessent said, “I agree that the Supreme Court reaffirmed your ability to implement an embargo.” Bessent added that the U.S. Trade Representative and Commerce Department would “begin investigations and we’ll move forward with those.”
A representative from the U.S. Treasury Department did not respond to a request from The Associated Press for additional comment.
Sánchez has been critical of the U.S. and Israeli attacks on Iran, calling it an “unjustifiable” and “dangerous” military intervention. His government has demanded an immediate de-escalation and dialogue and also condemned Iran’s strikes across the region.
Trump said, “Spain has absolutely nothing that we need other than great people. They have great people, but they don’t have great leadership.”
Spain’s position on the use of U.S. bases in its territory marks the latest flare-up in its relationship with the Trump administration. Under Sánchez, Europe’s last major progressive leader, Spain was also an outspoken critic of Israel’s war in Gaza.
___
Naishadham reported from Madrid. AP journalist Sam McNeil in Brussels contributed.
-

 The Dictatorship1 year ago
The Dictatorship1 year agoLuigi Mangione acknowledges public support in first official statement since arrest
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoFormer ‘Squad’ members launching ‘Bowman and Bush’ YouTube show
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoBlue Light News’s Editorial Director Ryan Hutchins speaks at Blue Light News’s 2025 Governors Summit
-

 The Dictatorship6 months ago
The Dictatorship6 months agoMike Johnson sums up the GOP’s arrogant position on military occupation with two words
-

 Politics1 year ago
Politics1 year agoFormer Kentucky AG Daniel Cameron launches Senate bid
-

 The Dictatorship1 year ago
The Dictatorship1 year agoPete Hegseth’s tenure at the Pentagon goes from bad to worse
-
Uncategorized1 year ago
Bob Good to step down as Freedom Caucus chair this week
-

 Politics11 months ago
Politics11 months agoDemocrat challenging Joni Ernst: I want to ‘tear down’ party, ‘build it back up’


