The Dictatorship
US signs new health deals with 9 African countries

JOHANNESBURG (AP) — The U.S. government has signed health deals with at least nine African countries, part of its new approach to global health fundingwith agreements that reflect the Trump administration’s interests and priorities and are geared toward providing less aid and more mutual benefits.
The agreements signed so far, with KenyaNigeria and Rwanda among others, are the first under the new global health framework, which makes aid dependent on negotiations between the recipient country and the U.S.
Some of the countries that have signed deals either have been hit by U.S. aid cuts or have separate agreements with the Trump administration to accept and host third-country deporteesalthough officials have denied any linkage.
The Trump administration says the new “America First” global health funding agreements are meant to increase self-sufficiency and eliminate what it says are ideology and waste from international assistance. The deals replace a patchwork of previous health agreements under the now-dismantled United States Agency for International Development.
U.S. aid cuts have crippled health systems across the developing world, including in Africawhere many countries relied on the funding for crucial programs, including those responding to outbreaks of disease.
The new approach to global health aligns with President Donald Trump’s pattern of dealing with other nations transactionallyusing direct talks with foreign governments to promote his agenda abroad. It builds on his sharp turn from traditional U.S. foreign assistance, which supporters say furthered American interests by stabilizing other countries and economies and building alliances.
A different strategy
The deals mark a sharp departure from how the U.S. has provided health care funding over the years and mirrors the Trump administration’s interests.
South Africa, which has lost most of its U.S. funding — including $400 million in annual support — due in part to its disputes with the U.S., has not signed a health deal, despite having one of the world’s highest HIV prevalence rates.
Nigeria, Africa’s most populous country, reached a deal but with an emphasis on Christian-based health facilities, although it has a slight majority Muslim population. Rwanda and Uganda, which each have deportation deals with the U.S., have announced the health pacts.
Cameroon, Eswatini, Lesotho, Liberia and Mozambique also are among those that have signed health deals with the U.S.
According to the Center for Global Development, a Washington think tank, the deals “combine U.S. funding reductions, ambitious co-financing expectations, and a shift toward direct government-to-government assistance.”
The deals represent a reduction in total U.S. health spending for each country, the center said, with annual U.S. financial support down 49% compared with 2024.
A faith-based deal in Nigeria, a lifeline for several others
Under its deal, Nigeria, a major beneficiary of USAID funds, would get support that has a “strong emphasis” on Christian faith-based health care providers.
The U.S. provided approximately $2.3 billion in health assistance to Nigeria between 2021 and 2025, mostly through USAID, official data shows. The new five-year agreement will see U.S. support at over $2 billion, while Nigeria is expected to raise $2.9 billion to boost its health care programs.
The agreement “was negotiated in connection with reforms the Nigerian government has made to prioritize protecting Christian populations from violence and includes significant dedicated funding to support Christian health care facilities,” the State Department said in a statement.
The department said “the president and secretary of state retain the right to pause or terminate any programs which do not align with the national interest,” urging Nigeria to ensure “that it combats extremist religious violence against vulnerable Christian populations.”
For several other countries, the new deals could be a lifeline after U.S. aid cuts crippled their health care systems and left them racing to fill the gaps.
Under its deal, Mozambique will get U.S. support of over $1.8 billion for HIV and malaria programs. Lesotho, one of the poorest countries in the world, clinched a deal worth over $232 million.
In the tiny kingdom of Eswatini, the U.S. committed to provide up to $205 million to support public health data systems, disease surveillance and outbreak response, while the country agreed to increase domestic health expenditures by $37 million.
No deal for South Africa after disputes
South Africa is noticeably absent from the list of signatories following tensions with the Trump administration.
Trump has said he will cut all financial assistance to South Africa over his widely rejected claims that it is violently persecuting its Afrikaner white minority.
The dismantling of USAID resulted in the loss of over $436 million in yearly financing for HIV treatment and prevention in South Africa, putting the program and thousands of jobs in the health care industry at risk.
Health compacts with countries that signed deportation deals
At least four of the countries that have reached deals previously agreed to receive third-country deportees from the U.S., a controversial immigration policy that has been a trademark of the Trump administration.
The State Department has denied any linkage between the health care compacts and agreements regarding accepting third-country asylum seekers or third-country deportees from the United States. However, officials have said that political considerations unrelated to health issues may be part of the negotiations.
Rwanda, one of the countries with a deportation deal with the U.S., signed a $228 million health pact requiring the U.S. to support it with $158 million.
Uganda, another such country, signed a health deal worth nearly $2.3 billion in which the U.S. will provide up to $1.7 billion. Also Eswatini, which has started receiving flights with deported prisoners from the U.S.
___
Associated Press writers Evelyne Musambi in Nairobi, Kenya, Dyepkazah Shibayan in Abuja, Nigeria, Mark Banchereau in Dakar, Senegal, and Matthew Lee in Washington contributed to this report.
The Dictatorship
Trump signs executive order to protect Venezuelan oil revenue
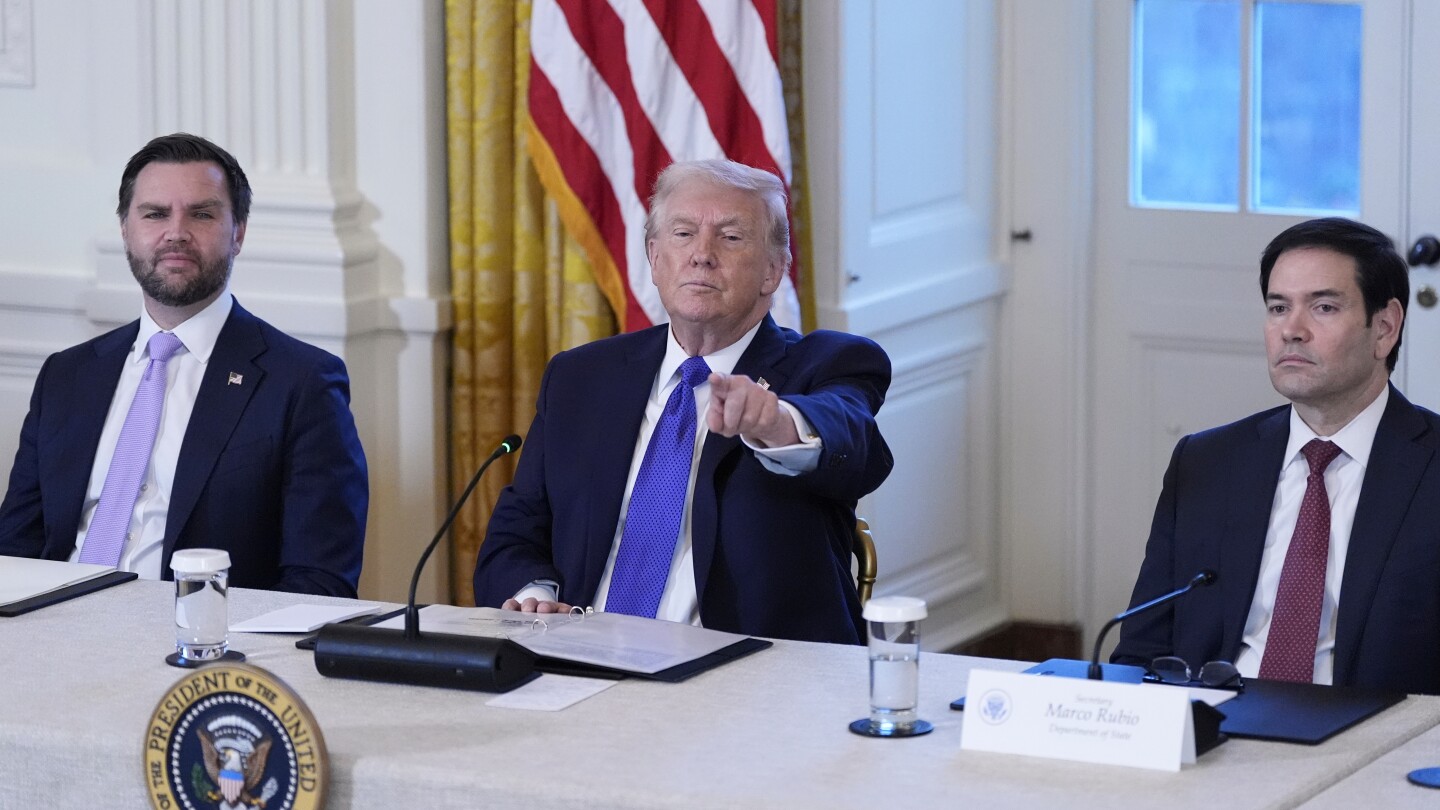

WEST PALM BEACH, Fla. (AP) — President Donald Trump’s new executive order on Venezuelan oil revenue is meant to ensure that the money remains protected from being used in judicial proceedings.
The executive order, made public on Saturday, says that if the funds were to be seized for such use, it could “undermine critical U.S. efforts to ensure economic and political stability in Venezuela.”
The order comes amid caution from top oil company executives that the tumult and instability in Venezuela could make the country less attractive for private investment and rebuilding.
“If we look at the commercial constructs and frameworks in place today in Venezuela, today it’s uninvestable,” said Darren Woods, CEO of ExxonMobil, the largest U.S. oil company, during a meeting convened by Trump with oil executives on Friday.
During the session, Trump tried to assuage the concerns of the oil companies and said the executives would be dealing directly with the U.S., rather than the Venezuelan government.
Venezuela has a history of state asset seizures, ongoing U.S. sanctions and decades of political uncertainty.
Getting U.S. oil companies to invest in Venezuela and help rebuild the country’s infrastructure is a top priority of the Trump administration after the dramatic capture of now-deposed leader Nicolás Maduro.
The White House is framing the effort to “run” Venezuela in economic terms, and Trump has seized tankers carrying Venezuelan oil, has said the U.S. is taking over the sales of 30 million to 50 million barrels of previously sanctioned Venezuelan crude, and plans to control sales worldwide indefinitely.
“I love the Venezuelan people, and am already making Venezuela rich and safe again,” Trump, who is currently in southern Florida, wrote on his social media site on Saturday. “Congratulations and thank you to all of those people who are making this possible!!!”
The order says the oil revenue is property of Venezuela that is being held by the United States for “governmental and diplomatic purposes” and not subject to private claims.
Its legal underpinnings are the National Emergencies Act and the International Emergency Economic Powers Act. Trump, in the order, says the possibility that the oil revenues could be caught up in judicial proceedings constitutes an “unusual and extraordinary threat” to the U.S.
The Dictatorship
Changes to the US vaccine recommendations are sowing confusion and could harm kids
Dr. Molly O’Shea has noticed growing skepticism about vaccines at both of her Michigan pediatric offices and says this week’s unprecedented and confusing changes to federal vaccine guidance will only make things worse.
One of her offices is in a Democratic area, where more of the parents she sees are opting for alternative schedules that spread out shots. The other is in a Republican area, where some parents have stopped immunizing their children altogether.
She and other doctors fear the new recommendations and the terminology around them will stoke vaccine hesitancy even more, pose challenges for pediatricians and parents that make it harder for kids to get shots, and ultimately lead to more illness and death.
The biggest change was to stop blanket recommendations for protection against six diseases and recommend those vaccines only for at-risk children or through something called “shared clinical decision-making” with a health care provider.
The phrase, experts say, is confusing and dangerous: “It sends a message to a parent that actually there’s only a rarefied group of people who really need the vaccine,” O’Shea said. “It’s creating an environment that puts a sense of uncertainty about the value and necessity or importance of the vaccines in that category.”
Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr.who helped lead the anti-vaccine movement for years, said in announcing the changes that they better align the U.S. with peer nations “while strengthening transparency and informed consent.”
But doctors say they are sowing doubt — the vaccines have been extensively studied and proven to be safe and effective at shielding kids from nasty diseases — at a time when childhood vaccination rates are already falling and some of those infectious diseases are spreading.
On Friday, the American Academy of Pediatrics and more than 200 medical, public health and patient advocacy groups sent a letter to Congress about the new childhood immunization schedule.
“We urge you to investigate why the schedule was changed, why credible scientific evidence was ignored, and why the committee charged with advising the HHS Secretary on immunizations did not discuss the schedule changes as a part of their public meeting process,” they wrote.
Many don’t know what ’shared decision-making’ means
O’Shea said she and other pediatricians discuss vaccines with parents at every visit where they are given. But that’s not necessarily “shared clinical decision-making,” which has a particular definition.
On its website, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices says: “Unlike routine, catch-up, and risk-based recommendations, shared clinical decision-making vaccinations are not recommended for everyone in a particular age group or everyone in an identifiable risk group. Rather, shared clinical decision-making recommendations are individually based and informed by a decision process between the health care provider and the patient or parent/guardian.”
In this context, health care providers include primary care physicians, specialists, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, registered nurses and pharmacists.
A pair of surveys conducted last year by the Annenberg Public Policy Center at the University of Pennsylvania suggested that many people don’t fully understand the concept, which came up last year when the federal government changed recommendations around COVID-19 vaccinations.
Only about 2 in 10 U.S. adults knew that one meaning behind shared decision-making is that “taking the vaccine may not be a good idea for everyone but would benefit some.” And only about one-third realized pharmacists count as health care providers to talk with during the process, even though they frequently administer vaccines.
As of this week, vaccines that protect against hepatitis A, hepatitis B, rotavirus, RSV, flu and meningococcal disease are no longer universally recommended for kids. RSV, hepatitis A, hepatitis B and meningococcal vaccines are recommended for certain high-risk populations; flu, rotavirus, hepatitis A, hepatitis B and meningococcal vaccines are recommended through shared decision-making — as is the COVID-19 vaccine, although that change was made last year.
Shortly after the federal announcement Monday, Dr. Steven Abelowitz heard from half a dozen parents. “It’s causing concern for us, but more importantly, concern for parents with kids, especially young kids, and confusion,” said Abelowitz, founder of Ocean Pediatrics in Orange County, California.
Though federal recommendations are not mandates — states have the authority to require vaccinations for schoolchildren — they can affect how easy it is for kids to get shots if doctors choose to follow them.
Under the new guidelines, O’Shea said, parents seeking shots in the shared decision-making category might no longer bring their kids in for a quick, vaccine-only appointment with staff. They’d sit down with a health care provider and discuss the vaccine. And it could be tougher to have a flu clinic, where parents drive up and kids get shots without seeing a doctor.
Staying the course as challenges mount
Still, doctors say they won’t let the changes stop them from helping children get the vaccines they need. Leading medical groups are sticking with prior vaccine recommendations. Many parents are, too.
Megan Landry, whose 4-year-old son Zackary is one of O’Shea’s patients, is among them.
“It’s my responsibility as a parent to protect my child’s health and well-being,” she said. “Vaccines are a really effective and well-studied way to do that.”
She plans to keep having the same conversations she’s always had with O’Shea before getting vaccines for Zackary.
“Relying on evidence and trusted medical guidance really helps me to make those decisions,” she said. “And for me, it’s not just a personal choice for my own son but a way to contribute to the health of everybody.”
But for other families, confidence about vaccines is waning as trust in science erodes. O’Shea lamented that parents are getting the message that they can’t trust medical experts.
“If I take my car to the mechanic, I don’t go do my own research ahead of time,” she said. “I go to a person I trust and I trust them to tell me what’s going on.”
Abelowitz, the California doctor, likened the latest federal move to pouring gasoline on a fire of mistrust that was already burning.
“We’re worried the fire’s out of control,” he said. “Already we’ve seen that with measles and pertussis, there are increased hospitalizations and even increasing deaths. So the way that I look at it — and my colleagues look at it — we’re basically regressing decades.”
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
The Dictatorship
U.S. launches fresh strikes on ISIS targets in Syria
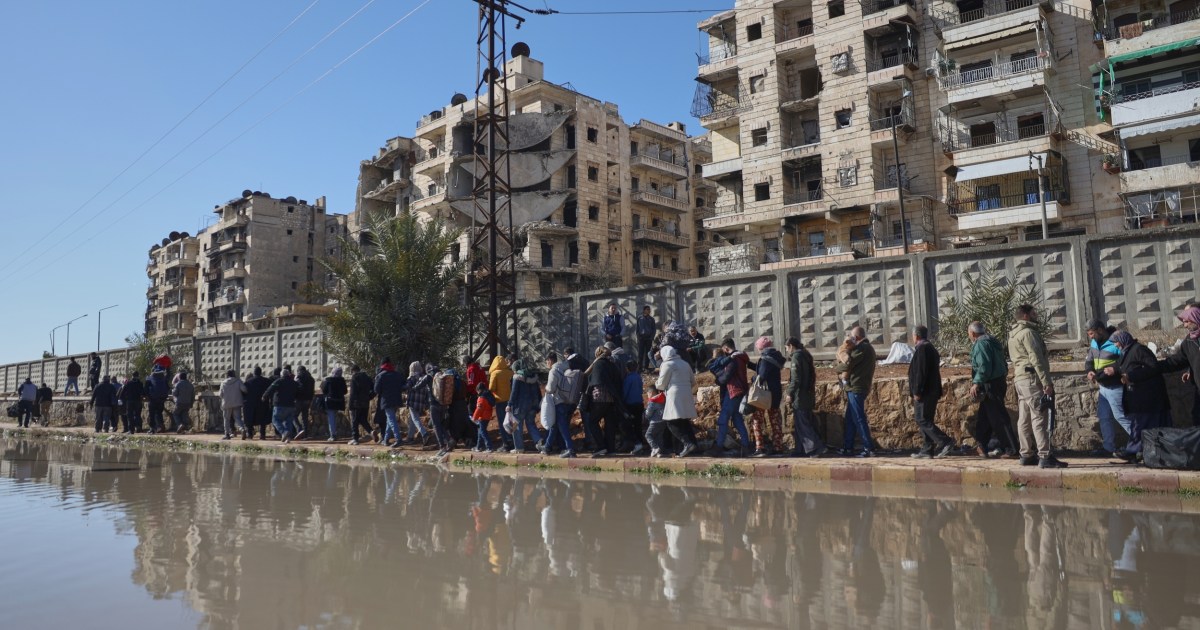

The U.S. has carried out “large-scale strikes” against multiple Islamic State targets in Syria along with partner forces, U.S. Central Command said on Saturday.
The attack is a part of an operation launched on Dec. 19, when U.S. forces struck “more than 70 targets” in central Syria as retaliation for the killing of three Americans by an ISIS gunman in early December.
“The strikes today targeted ISIS throughout Syria as part of our ongoing commitment to root out Islamic terrorism against our warfighters, prevent future attacks, and protect American and partner forces in the region,” CENTCOM said in a statement.
Tom Barrack, the Trump administration’s special envoy for Syria, announced on Saturday that he met with Syria’s new leadership in Damascus “to discuss recent developments in Aleppo and the broader path forward for Syria’s historic transition.”
The deadly attack in December marked the first fatalities of U.S. troops in the country since former President Bashar al-Assad was ousted last year. Three other U.S. service members were injured in the attack in December, and a state-run news agency reported that two members of the Syrian security forces were also wounded.
President Donald Trump said at the time that the attack by ISIS took place “in a very dangerous part of Syria, that is not fully controlled by them.” He also said Syrian President Ahmed al-Sharaa, whom he had met in November at the White House, was “extremely angry and disturbed by this attack.”
Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said last month that the operation was “a declaration of vengeance” over the deaths of the American service members.
This is a developing story. Please check back for updates.
Clarissa-Jan Lim is a breaking news reporter for MS NOW. She was previously a senior reporter and editor at BuzzFeed News.
-

 The Dictatorship11 months ago
The Dictatorship11 months agoLuigi Mangione acknowledges public support in first official statement since arrest
-

 The Dictatorship4 months ago
The Dictatorship4 months agoMike Johnson sums up the GOP’s arrogant position on military occupation with two words
-

 Politics11 months ago
Politics11 months agoBlue Light News’s Editorial Director Ryan Hutchins speaks at Blue Light News’s 2025 Governors Summit
-

 Politics11 months ago
Politics11 months agoFormer ‘Squad’ members launching ‘Bowman and Bush’ YouTube show
-

 Politics11 months ago
Politics11 months agoFormer Kentucky AG Daniel Cameron launches Senate bid
-

 The Dictatorship11 months ago
The Dictatorship11 months agoPete Hegseth’s tenure at the Pentagon goes from bad to worse
-
Uncategorized1 year ago
Bob Good to step down as Freedom Caucus chair this week
-

 Politics9 months ago
Politics9 months agoDemocrat challenging Joni Ernst: I want to ‘tear down’ party, ‘build it back up’